 Jeep Cherokee Service ManualTransmission and transfer case » Automatic transmission-30RH » Description and operation
Jeep Cherokee Service ManualTransmission and transfer case » Automatic transmission-30RH » Description and operation
Servos
Servos
DESCRIPTION
KICKDOWN (FRONT) SERVO
The kickdown servo (Fig. 49) consists of a two-land piston with an inner piston, a piston rod and guide, and a return spring. The dual-land piston uses seal rings on its outer diameters and an O-ring for the inner piston.
LOW/REVERSE (REAR) SERVO
The rear (low/reverse) servo consists of a single stage or diameter piston and a spring loaded plug.
The spring is used to cushion the application of the rear (low/reverse) band.
OPERATION
KICKDOWN (FRONT) SERVO
The application of the piston is accomplished by applying pressure between the two lands of the piston.
The pressure acts against the larger lower land to push the piston downward, allowing the piston rod to extend though its guide against the apply lever.
Release of the servo at the 2-3 upshift is accomplished by a combination of spring and line pressure, acting on the bottom of the larger land of the piston.
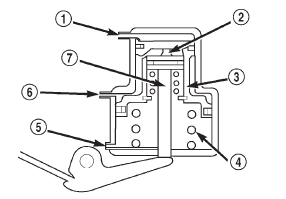
Fig. 49 Front Servo
1 - VENT
2 - INNER PISTON
3 - PISTON
4 - SPRING
5 - RELEASE PRESSURE
6 - APPLY PRESSURE
7 - PISTON ROD
The small piston is used to cushion the application of the band by bleeding oil through a small orifice in the larger piston. The release timing of the kickdown servo is very important to obtain a smooth but firm shift. The release has to be very quick, just as the front clutch application is taking place. Otherwise, engine runaway or a shift hesitation will occur. To accomplish this, the band retains its holding capacity until the front clutch is applied, giving a small amount of overlap between them.
LOW/REVERSE (REAR) SERVO
While in the de-energized state (no pressure applied), the piston is held up in its bore by the piston spring. The plug is held down in its bore, in the piston, by the plug spring. When pressure is applied to the top of the piston, the plug is forced down in its bore, taking up any clearance. As the piston moves, it causes the plug spring to compress, and the piston moves down over the plug. The piston continues to move down until it hits the shoulder of the plug and fully applies the band. The period of time from the initial application, until the piston is against the shoulder of the plug, represents a reduced shocking of the band that cushions the shift.
30RH automatic transmission
Fluid
Torque converter
Oil pump
Valve body
Accumulator
Pistons
Front clutch
Rear clutch
Overrunning clutch
Planetary gearset
Bands
Servos
Governor
Gearshift mechanism
Converter drainback valve
Brake transmission shift interlock mechanism
Jeep Cherokee Service Manual
- Lubrication and maintenance
- Suspension
- Differential and driveline
- Brakes
- Clutch
- Cooling system
- Battery
- Starting systems
- Charging system
- Ignition system
- Instrument panel systems
- Audio systems
- Horn systems
- Speed control system
- Turn signal and hazard warning systems
- Wiper and washer systems
- Lamps
- Passive restraint systems
- Electrically heated systems
- Power distribution systems
- Power lock systems
- Vehicle theft/security systems
- Power seat systems
- Power window systems
- Power mirror systems
- Chime/buzzer warning systems
- Overhead console systems
- Engine
- Exhaust system
- Frame and bumpers
- Frame
- Fuel system
- Steering
- Transmission and transfer case
- Tires and wheels
- Body
