Jeep Cherokee (XJ): Starting system
DIAGNOSIS
The battery, starting system and charging system in the vehicle operate with one another, and must be tested as a complete system. In order for the engine to start and the battery to charge properly, all of the components that are used in these systems must perform within specifications. The service information for these systems has been separated within this service manual to make it easier to locate the specific information you are seeking. However, when attempting to diagnose any of these systems, it is important that you keep their interdependency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used for the battery, starting system and charging system include the most basic conventional diagnostic methods, to the more sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Use of an induction-type milliampere ammeter, a volt/ohmmeter, a battery charger, a carbon pile rheostat (load tester) and a 12-volt test lamp may be required. All OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in electronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to Charging System, On-Board Diagnostic Test in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper on-board diagnostic test procedures.
|
Starting System Diagnosis |
||
|
Condition |
Possible Cause |
Correction |
| Starter fails to operate |
|
|
| Starter engages, fails to turn engine. |
|
|
| Starter engages, spins out before engine starts. |
|
|
| Starter does not disengage |
|
|
TESTING
Before testing the starting system perform a visual inspection of the starting system components and connections. Refer to Starting System in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper starting system cleaning and inspection procedures.
COLD CRANKING TEST
Refer to Starting System in the index of this service manual for the location of complete starting system wiring diagrams. Before performing this test, be certain that the following procedures are accomplished:
- The battery is fully-charged and load tested. Refer to Battery Charging in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper battery charging procedures. Refer to Battery in the index of this service manual for the location of the battery diagnosis and testing procedures, including the proper battery load test procedures.
- Fully engage the parking brake.
- If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the Park position. If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the Neutral position and block the clutch pedal in the fully depressed position.
- Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned off.
- To prevent the engine from starting, remove the Automatic ShutDown (ASD) relay. The ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC), in the engine compartment. See the fuse and relay layout label affixed to the underside of the PDC cover for ASD relay identification and location.
(1) Connect a suitable volt-ampere tester to the battery terminals (Fig. 3). See the instructions provided by the manufacturer of the volt-ampere tester being used.
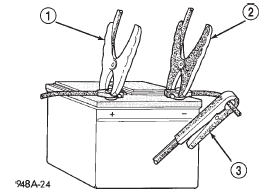
Fig. 3 Volts-Amps Tester Connections - Typical
1 - POSITIVE CLAMP
2 - NEGATIVE CLAMP
3 - INDUCTION AMMETER CLAMP
(2) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the Start position. Note the cranking voltage and current (amperage) draw readings shown on the volt-ampere tester.
(a) If the voltage reads below 9.6 volts, refer to Starter Motor in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper starter motor diagnosis and testing procedures. If the starter motor tests OK, refer to Engine Diagnosis in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper engine diagnosis and testing procedures. If the starter motor is not OK, replace the faulty starter motor.
(b) If the voltage reads above 9.6 volts and the current (amperage) draw reads below specifications, refer to the Feed Circuit Test in this section.
(c) If the voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and the starter motor does not turn, refer to the Control Circuit Test in this section.
(d) If the voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and the starter motor turns very slowly, refer to the Feed Circuit Test in this section.
NOTE: A cold engine will increase the starter current (amperage) draw reading, and reduce the battery voltage reading.
FEED CIRCUIT TEST
The starter feed circuit test (voltage drop method) will determine if there is excessive resistance in the high-amperage starter feed circuit. Refer to Starting System in the index of this service manual for the location of complete starting system wiring diagrams.
When performing the voltage drop test, it is important to remember that the voltage drop is giving an indication of the resistance between the two points at which the voltmeter probes are attached. EXAMPLE: When testing the resistance of the battery positive cable, touch the voltmeter leads to the battery positive cable terminal clamp and to the battery positive cable eyelet terminal at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud. If you probe the battery positive terminal post and the battery positive cable eyelet terminal at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud, you are reading the combined voltage drop in the battery positive cable terminal clamp-to-terminal post connection and the battery positive cable.
The following operation will require a voltmeter accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing this test, be certain that the following procedures are accomplished:
- The battery is fully-charged and load tested. Refer to Battery Charging in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper battery charging procedures. Refer to Battery in the index of this service manual for the location of the battery diagnosis and testing procedures, including the proper battery load test procedures.
- Fully engage the parking brake.
- If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the Park position. If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the Neutral position and block the clutch pedal in the fully depressed position.
- Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned off.
- To prevent the engine from starting, remove the Automatic ShutDown (ASD) relay. The ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC), in the engine compartment. See the fuse and relay layout label affixed to the underside of the PDC cover for ASD relay identification and location.
(1) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to the battery negative terminal post. Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to the battery negative cable terminal clamp (Fig. 4). Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct the poor contact between the battery negative cable terminal clamp and the battery negative terminal post.
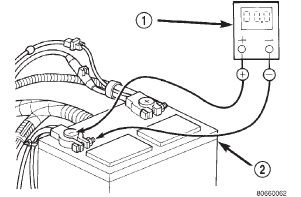
Fig. 4 Test Battery Negative Connection Resistance - Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
(2) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to the battery positive terminal post. Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to the battery positive cable terminal clamp (Fig. 5). Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct the poor connection between the battery positive cable terminal clamp and the battery positive terminal post.
(3) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the battery positive cable terminal clamp and the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud (Fig. 6). Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the voltmeter. If the reading is above 0.2 volt, clean and tighten the battery positive cable eyelet terminal connection at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud.
Repeat the test. If the reading is still above 0.2 volt, replace the faulty battery positive cable.
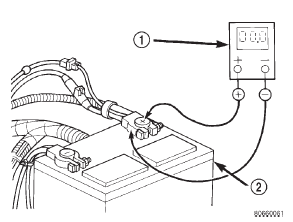
Fig. 5 Test Battery Positive Connection Resistance - Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
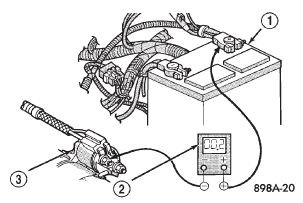
Fig. 6 Test Battery Positive Cable Resistance -
Typical
1 - BATTERY
2 - VOLTMETER
3 - STARTER MOTOR
(4) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the battery negative cable terminal clamp and a good clean ground on the engine block (Fig. 7). Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the Start position.
Observe the voltmeter. If the reading is above 0.2 volt, clean and tighten the battery negative cable eyelet terminal connection to the engine block.
Repeat the test. If the reading is still above 0.2 volt, replace the faulty battery negative cable.
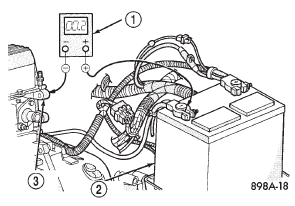
Fig. 7 Test Ground Circuit Resistance - Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
3 - ENGINE GROUND
(5) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to the starter housing. Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to the battery negative terminal post (Fig.
8). Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the voltmeter. If the reading is above 0.2 volt, correct the poor starter to engine block ground contact.
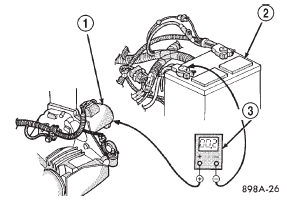
Fig. 8 Test Starter Ground - Typical
1 - STARTER MOTOR
2 - BATTERY
3 - VOLTMETER
If the resistance tests detect no feed circuit problems, refer to Starter Motor in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper starter motor diagnosis and testing procedures.
CONTROL CIRCUIT TEST
The starter control circuit components should be tested in the order in which they are listed, as follows:
- Starter Relay Refer to Starter Relay in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper starter relay diagnosis and testing procedures.
- Starter Solenoid Refer to Starter Motor in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper starter solenoid diagnosis and testing procedures.
- Ignition Switch Refer to Ignition Switch and Key Lock Cylinder in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper ignition switch diagnosis and testing procedures.
- Clutch Pedal Position Switch If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmission, refer to Clutch Pedal Position Switch in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper clutch pedal position switch diagnosis and testing procedures.
- Park/Neutral Position Switch If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic transmission, refer to Park/Neutral Position Switch in the index of this service manual for the location of the proper park/ neutral position switch diagnosis and testing procedures.
 Starter motor noise - 2.5L engine. Starter motor. Starter relay
Starter motor noise - 2.5L engine. Starter motor. Starter relay
Other materials:
Customer Programmable Features/Personal Settings - Uconnect 5.0 Settings
Push the SETTINGS or the MORE button on the faceplate,
then the "Settings" button on the touchscreen (if
equipped) to display the menu setting screen. In this
mode the Uconnect system allows you to access programmable
features that may be equipped such as Display,
Voice, Clock & Date, Safet ...

